Industry-funded item of the week: artificial sweeteners
Hand Cardullo writes in Forbes: 87% Of Sweetened Products Contain Added Sugars Only, Study Finds.
That seemed interesting. But then I got to the sub-headline: New Georgetown University report cites need for more low- and no-calorie sweeteners.
As public health officials clamor to remove added sugars from food and beverage products, a new study published by the Georgetown University Business for Impact Center signals that there is much heavy lifing ahead (full disclosure: I served as an author of the paper). The report noted that added sugars dominate products containing sweeteners, with 87% of items formulated this way. Only 8% of sweetened items contain low- or no-calorie sweeteners (LNCS) only, with 5% consisting of a combination of the two. The paper concluded that increased use of LNCS was necessary to eliminate meaningful amounts of added sugars and that LNCS offered effective and safe ways to do so.
Cardullo says: “Here are some things to consider:
- If public health organizations want to achieve their added sugar reduction goals, they must step up and communicate the efficacy and safety of LNCS in helping consumers manage and lose weight. This will go a long way in helping to clear up consumer confusion.
- The evidence suggests that the public health community must use only the best studies to advance firm points of view on the use of LNCS.
- To help reduce added sugars, food and beverage companies should incorporate LNCS into more of their products.”
Really? My usual question: Who paid for this?
The paper: Moving Towards Healthier Eating Habits: Why Low- and No-Calorie Sweeteners Play a Critical Role
The funder: “Funding for this paper was provided by the Calorie Control Council” [an international association representing the low- and reduced-calorie food and beverage industry].
Comment: Here is one of the figures from the paper.
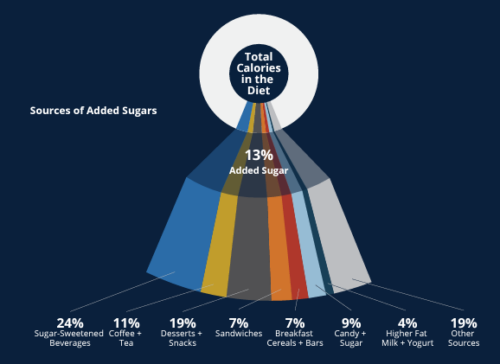
This shows that 24% of added sugars come from sugar-sweetened beverages, and another 19% come from desserts and snacks.
Cutting down on both is a good idea on its own, and one that does not require the addition or substitution of artificial sweetneners.

