USDA announces COVID-19 food assistance
The USDA has established a new Coronavirus Food Assistance Program (CFAP).
This has $19 billion to distribute to farmers, ranchers, and consumers.
Cutting through the rhetoric, the new program has two parts:
- Direct Support to Farmers and Ranchers—$16 billion: for direct support and marketing costs. [Note: producers say this is not enough].
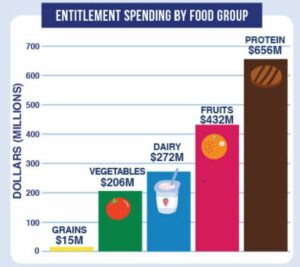
- USDA Purchase and Distribution—$3 billion: for buying fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, and meat products at the rate of $100 million per month, each. “The distributors and wholesalers will then provide a pre-approved box of fresh produce, dairy, and meat products to food banks, community and faith based organizations, and other non-profits serving Americans in need.” [Note: Fruit and vegetable producers say this is not enough].
In addition, the USDA says it will:
- Allocate $873.3 million to purchase a variety of agricultural products for distribution to food banks, as determined by industry requests, USDA agricultural market analysis, and food bank needs.
- Under previous acts, allocate $850 million for food bank administrative costs and USDA food purchases, of which a minimum of $600 million will be designated for food purchases, as determined by food bank need and product availability.
Comment
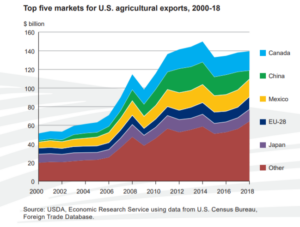
- The bulk of this program goes to Big Ag—on top of the $22 billion or so Big Ag got in compensation for trade losses last year.
- The much smaller Purchase and Distribution program is to deal with the shocking problem of producers destroying foods while hungry people line up for food distribution from food banks overwhelmed by the demand.
- USDA is using this to reinstate its “harvest box” proposals as a means to replace SNAP benefits.
- USDA is not backing off from its other long-term strategy to do all it can to reduce SNAP enrollments and benefits, or from Trump Administration public charge policies that put anyone who is not a citizen at risk of never getting citizenship or of deportation if they apply for public benefits.
- These measures are expensive band-aids. They do not address fundamental flaws in agricultural support programs.
- Maybe this crisis will at last cause Congress to start supporting sustainable, resiliant agriculture? Hey, I can dream.
Here is everything else the USDA says it is doing
the USDA announcement also says what it is already doing “to make sure children and families are fed during a time of school closures and job losses, as well as increase flexibilities and extensions in USDA’s farm programs to ensure the U.S. food supply chain remains safe and secure.” What follows is a direct quote.
Feeding Kids and Families
- USDA expanded flexibilities and waivers in all 50 states and territories to ensure kids and families who need food can get it during this national emergency.
- USDA is partnering with the Baylor Collaborative on Hunger and Poverty, McLane Global, PepsiCo, and others to deliver more than 1,000,000 meals a week to students in a limited number of rural schools closed due to COVID-19.
- USDA authorized Pandemic EBT in Michigan and Rhode Island, a supplemental food purchasing benefit to current SNAP participants and as a new EBT benefit to other eligible households to offset the cost of meals that would have otherwise been consumed at school.
- USDA expanded an innovative SNAP online grocery purchase pilot program in Arizona and California, Florida and Idaho, and DC and North Carolina, in addition to Alabama, Iowa, Nebraska, New York, Oregon and Washington.
Actions to Ensure a Strong Food Supply Chain
- USDA is working to ensure the food supply remains safe and secure.
- USDA announced flexibilities to ensure food distribution for certain food products like dairy and eggs reach retail settings.
- USDA announced farm loan flexibilities, deferrals (PDF, 243 KB), and maturity extensions.
Whole of Government Response in Rural America
- USDA released The COVID-19 Federal Rural Resource Guide (PDF, 349 KB), a first-of-its-kind resource for rural leaders looking for federal funding and partnership opportunities to help address this pandemic.
- USDA opened a second application window (April 14, 2020 to July 13, 2020) for $72 million of funding under the Distance Learning and Telemedicine (DLT) grant program.
- USDA Rural Development lenders may offer 180-day loan payment deferrals without prior agency approval for Business and Industry Loan Guarantees, Rural Energy for America Program Loan Guarantees, Community Facilities Loan Guarantees, and Water and Waste Disposal Loan Guarantees.
- USDA will use the $100 million provided for the ReConnect Program in the CARES Act to invest in qualified 100 percent grant projects.
For all the information on USDA’s work during the COVID-19 pandemic and resources available, please visit www.usda.gov/coronavirus.