Meat alternatives: cell-based
I’m seeing considerable confusion about the difference between cell-based and plant-based meat alternatives.
Cell-based products are not yet on the market, except in Singapore. Plant-based products are everywhere, and I will deal with them separately tomorrow.
For an example of the confusion, Phil Howard’s op-ed in Civil Eats was first titled Giant Meat and Dairy Companies Are Dominating the Plant-Based Protein Market, but his informative diagram refers to cell-cultured meat and fish alternatives, those that start with cells of animal origin. Civil Eats, ever careful, fixed the headline so it now reads, Op-Ed: Giant Meat and Dairy Companies Are Dominating the Plant-Based and Cellular Meat Market.
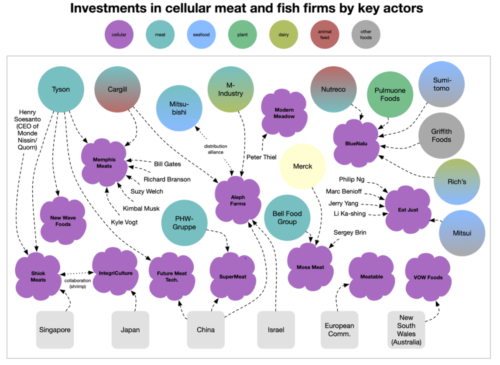
Today, lets stick to cell-based, beginning with Joe Fassler‘s thoughtful analysis in The Counter: “Lab-grown meat is supposed to be inevitable. The science tells a different story.”
That science tells us:
- Manufacturers consistently miss targets for product release.
- Production costs are astronomical.
- Even if costs can be reduced, production volume can never match real meat.
- Producing cell-based meat to scale means keeping it free of contaminants (difficult, if not impossible)
- Fetal blood serum, a necessary ingredient, requires animals to be slaughtered.
- Cell culture facilities are resource-intensive.
In the meantime, here are some of the latest developments in regulation, image, and celebrity investment.
- USDA seeks comments on labeling cell-based meat: The notice, available in the Federal Register online, is a step toward establishing a regulatory framework for these products.
- Cell-based disruption: How many factories, and at what capacity, are required to supply 10% of the meat market? If the cultivated meat industry were to set the ambitious target of supplying 10% of the global meat market, how much product would be required? How many factories, containing how many bioreactors, would need to be built? And where?… Read more
- Cell-based or cell-cultured: What’s the best name for next-gen seafood made from fish cells?
- With terminology ranging from cell-based to cell-cultured, cultivated, clean, and in vitro, how can consumer research help industry settle on one single term for next-gen seafood made from fish cells?… Read more
- Ad: How Aqua Cultured Foods plans to own the whole cut seafood analog space: Today Aqua Cultured Foods, a Chicago female-founded startup, announced their use of fermentation technology to create seafood alternatives with an incredibly realistic taste, texture, and nutritional profile…The company has developed whole-muscle cuts using biomass fermentation and a specific strain of fungi to deliver a high protein content comparable to cod, plus fiber and Omega-3s, without fat or cholesterol.
- Eat Just Raises $97 Million More to Fund Cultured Meat Production: The investment, which was part of a round announced in May that raised $170 million, came from new groups including Resilience Reserve, a venture capital fund, and existing backers like hedge fund UBS O’Connor and Graphene Ventures. This brings the round to $267 million, making it the largest ever for cultivated meat, which backers say will help to meet the world’s rising demand for animal products in a more humane and environmentally friendly way. Eat Just is also adding Dan Glickman, a former U.S. agriculture secretary, to its advisory board, and Jim Borel, a former executive at DuPont, to its board of directors.
- Leonardo DiCaprio invests in cultivated meat firms Mosa Meat and Aleph Farms: Cultured meat innovators Mosa Meat and Aleph Farms have secured the backing of high-profile investor Leonardo DiCaprio, known for his Academy Award winning roles as well as his environmental activism…. Read more
And here’s a summary of the latest research on concentration and power in cell-based agriculure.
- Democratizing ownership and participation in the 4th Industrial Revolution: challenges and opportunities in cellular agriculture: In this paper, we have sought to engage the nascent feld of cellular agriculture in conversation with the political economy of agriculture scholarship, namely, on the inescapable question of whether or not this emerging technology will further concentrate wealth and power in the global food system. Innovation without meaningful inclusion has led to inequality, distrust, environmental crises, and social disintegration, and the world’s biggest tech companies are well positioned to continue disrupting and absorbing traditional industries in the coming decades…Critically important and valuable innovation, including agroecological approaches to food production, also continues to come from non-industrial contexts.

