What’s up with Lucky Charms?
Hundreds of reports of illness from eating Lucky Charms cereal have intrigued food safety experts.
The FDA is investigating, but being really cagey about it.
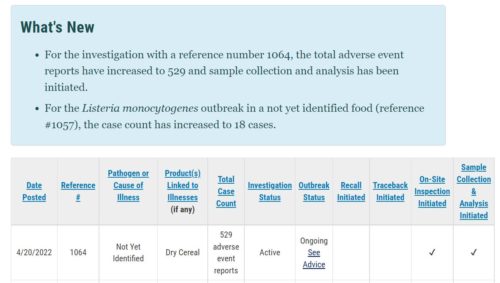
Everybody seems to know that reference number 1064 refers to Lucky Charms cereal.
The FDA has received 529 reports of adverse effects.
Food safety lawyer Bill Marler has been following the situation.
Since late 2021, the crowd sourcing website iwaspoisoned.com has received 6,400 reports from people complaining of classic food poisoning symptoms of nausea, vomiting and diarrhea after eating Lucky Charms cereal. General Mills, the maker of the cereal, has said that is has investigated the situation and there is no apparent link between the reported illnesses and Lucky Charms.
The Washington Post quotes experts calling for a recall, Bill Marler among them.
Although, there has been no scientific proven link, be it chemical or an allergen, between the several thousand illnesses and Lucky Charms,” Marler said, “my advice to General Mills is to recall the product and reset its trust with the consuming public until more is known.
Is there a link? Or is this just a matter of people getting sick, remembering they ate this cereal, and putting the two together—even though no cause-and-effect exists.
Ingredients. Whole Grain Oats, Sugar, Corn Starch, Modified Corn Starch, Corn Syrup, Dextrose. Contains 2% or less of: Salt, Gelatin, Trisodium Phosphate, Red 40, Yellow 5 & 6, Blue 1, Natural and Artificial Flavor.


