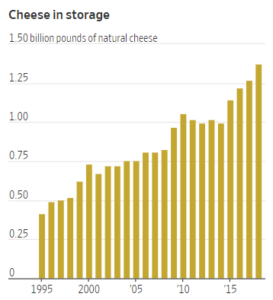
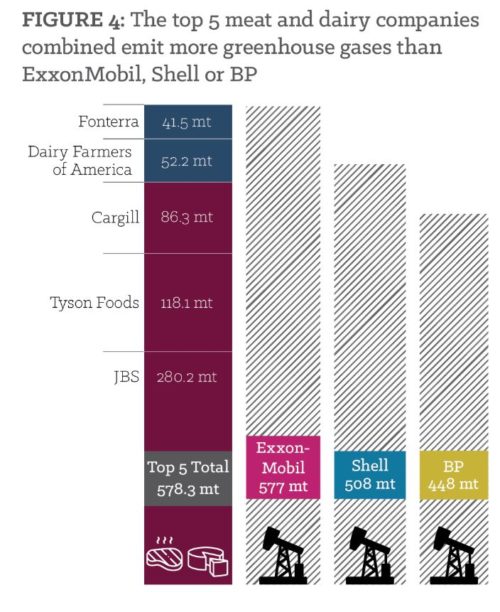
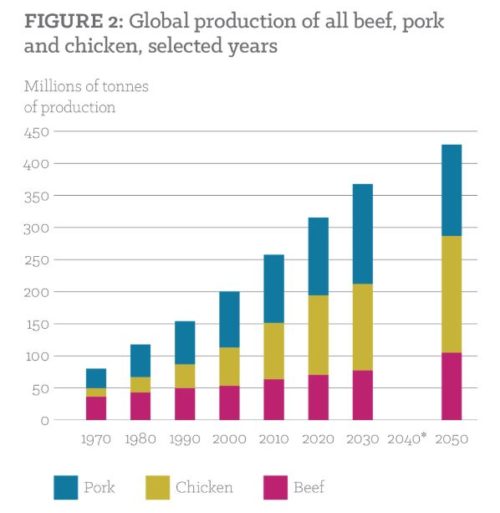
Christopher Gardner, the Stanford scientist who studies the ways various dietary patterns affect body weight, sent me this study to add to my post-book collection (I wrote about such things in Unsavory Truth: How Food Companies Skew the Science of What We Eat, just out).
Soon after Dr. Gardner sent this to me, I read about this study in DairyReporter.com. Its account had this headline: “Mediterranean diet with added dairy shown to improve heart health in Australia.” It said nothing about funding source (it should have).
The study:
Title: A Mediterranean diet supplemented with dairy foods improves markers of cardiovascular risk: results from the MedDairy randomized controlled trial. Alexandra T Wade, Courtney R Davis, Kathryn A Dyer, Jonathan M Hodgson, Richard J Woodman, and Karen J Murphy. Am J Clin Nutr 2018;108:1166–1182.
Rationale: The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) “may not meet Western recommendations for calcium and dairy intake.” Translation: Australians don’t eat enough dairy foods.
Objective: Determine the effect of a MedDiet supplemented with dairy foods (MedDairy) on blood pressure and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Design: The study compared the effects of consuming two different diets, (1) a MedDiet with 3–4 daily servings of dairy (MedDairy) versus (2) a lowfat control diet (LowFat).
Results: Participants on MedDairy reduced their blood pressure and other CVD risk factors.
Conclusion: “The MedDiet supplemented with dairy may be appropriate for an improvement in cardiovascular risk factors in a population at risk of CVD.”
Funding: “Supported by a Dairy Australia Research Grant.”
Dr. Gardner’s comments: the study does not compare the MedDiet to MedDairy. Instead, it compares MedDairy to LowFat—whatever people habitually eat, but restricted in fat.
In this study, compared to the LowFat group, the MedDairy group ate:
- More fat
- Less refined grain
- More legumes
- Less red meat
- More meat substitutes
- More nuts and seeds
- And, yes, more dairy (mostly yogurt)
Even so, the LowFat group lost more fat mass and gained more lean body mass than did the MedDairy group, but the authors do not mention that in the abstract and don’t make a big deal about it.
But they do say this in their discussion:
However, the use of an LF [LowFat] control diet may limit the generalizability of our results, as well as our capacity to evaluate the benefits of adding dairy to a traditional MedDiet.
Precisely.