The USDA is at long last giving some attention—a small but significant first step—to reducing Salmonella contamination of poultry products.
Salmonella is a big problem in poultry and eggs. For decades, food safety advocates have called on the USDA to declare Salmonella an adulterant. Adulterated food is illegal to sell.
The poultry industry has resisted, arguing that chicken gets cooked before it is eaten; cooking kills Salmonella.
It does, but you don’t want toxic forms of Salmonella in your kitchen where they can get into other foods. For background all this, see my book, Safe Food: The Politics of Food Safety.
In a press release, the USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) announces that it
is considering a regulatory framework for a new strategy to control Salmonella in poultry products and more effectively reduce foodborne Salmonella infections linked to these products…The most recent report from the Interagency Food Safety Analytics Collaboration estimates that over 23% of foodborne Salmonella illnesses are attributable to poultry consumption—almost
17% from chicken and over 6% from turkey.
The proposed Salmonalla framework has three components:
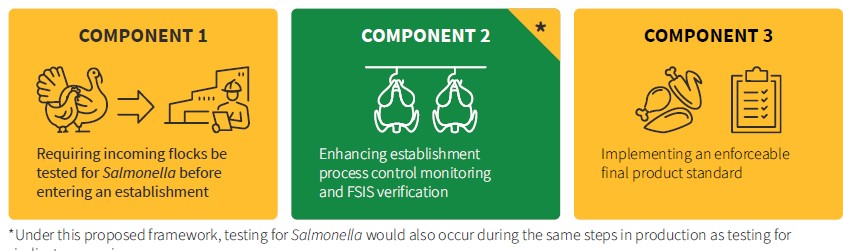
What FSIS is actually doing:
We will publish a proposed notice of determination to declare Salmonella an adulterant in NRTE [not ready to eat] breaded and stuffed chicken products in 2022, and we intend to publish additional proposed rules and policies implementing this strategy in 2023, with the goal of finalizing any rules by mid-2024.
The adulterant consideration only applies to breaded and stuffed chicken or turkey products that are likely to be microwaved but not necessarily thoroughly cooked. It does not apply to plain, unbreaded and unstuffed poultry.
Consumer Reports finds lots of poultry to be contaminated with Salmonella. Consumer Reports says Salmonella is “lethal but legal.”
Currently, a chicken processing facility is allowed to have salmonella in up to 9.8 percent of all whole birds it tests, 15.4 percent of all parts, and 25 percent of ground chicken. And producers that exceed these amounts are not prevented from selling the meat. If salmonella became an adulterant, even in some poultry products, it would help reduce the amount of contaminated meat that hits the market.
As might be expected, the National Chicken Council opposes the USDA’s proposed framework: “lacks data, research.”
the facts show that the Centers for Disease Control and FSIS’s own data demonstrate progress and clear reductions in Salmonella in U.S. chicken products. “Increased consumer education about proper handling and cooking of raw meat must be part of any framework going forward…Proper handling and cooking of poultry is the last step, not the first, that will help eliminate any risk of foodborne illness. We’ll do our part to promote safety.”
In other words, the poultry industry wants you to be responsible for protecting yourself against Salmonella. If only you would do a better job of handling and cooking raw chicken. It does not want to have to reduce Salmonella in its flocks in the first place (something quite possible, by the way).
This is a good first step. Let’s urge the USDA to go even further and declare Salmonella an adulterant on all poultry sold in supermarkets.
And maybe require poultry producers to do everything possible to prevent Salmonella geting into flocks in the first place.
This won’t be easy, according to a United Nations report from a recent expert meeting.
The expert consultation noted that no single control measure was sufficiently effective at reducing either the prevalence or the level of contamination of broilers and poultry meat with NT-Salmonella spp. Instead, it was emphasized that control strategies based on multiple intervention steps (multiple or multi-hurdle) would provide the greatest impact in controlling NT-Salmonella spp. in the broiler production chain.
The experts concluded that all of the following approaches were needed:
- Biosecurity and management
- Vaccination
- Antimicrobial
- Competitive exclusion/probiotics
- Feed and water
- Bacteriophage (bacterial viruses)
- Processing and post-processing interventions
***********
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.






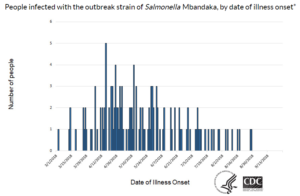
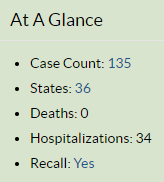 The Food Safety and Modernization Act set rules governing the safe production of foods. Clearly, some companies, this one apparently, did not bother to follow them.
The Food Safety and Modernization Act set rules governing the safe production of foods. Clearly, some companies, this one apparently, did not bother to follow them.