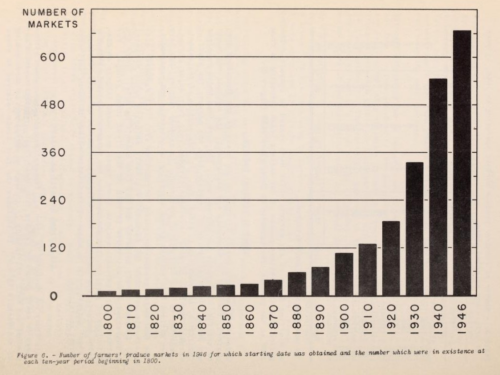
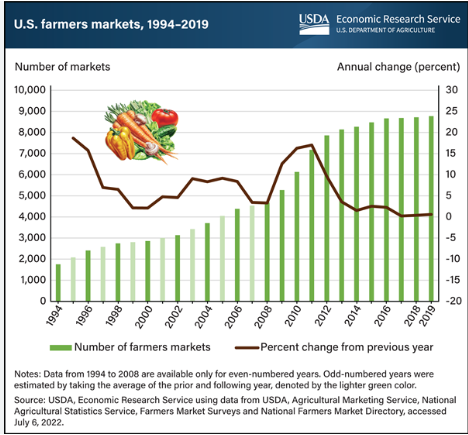
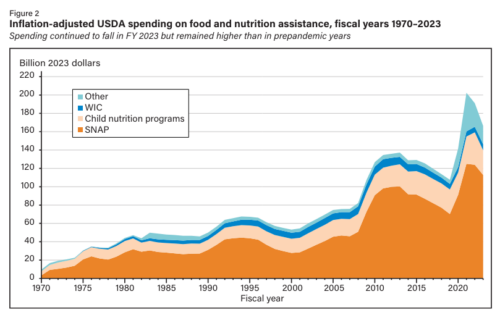
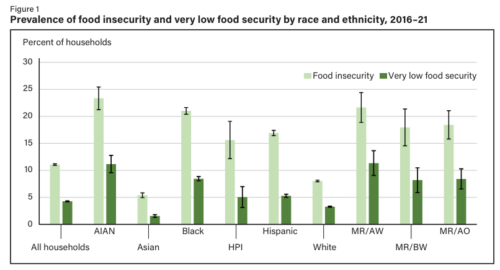
Industry marketing ploy of the week: Team Beef
Thanks to Hugh Joseph for this one: Running for the Ribeye.
Team Beef was created in 2009 by the national beef checkoff program, the marketing and research group that requires beef producers and importers to pay a $1-per-head on animals they market. The stated goal is to “promote beef’s health benefits and showcase people leading active and healthy lifestyles fueled by lean beef,” according to the Cattlemen’s Beef Board website. There are more than 20 teams across the country, each independently run by the respective state’s beef board.
…“Team Beef is a collection of runners and athletes … that believe in beef as a powerful protein to fuel their training and their everyday lives,” said Kentucky rancher Joe Lowe, in a promotional video that includes him cheersing his wife Cassie with beef jerky.
…Some states require that team members go through an online, self-guided course called Masters of Beef Advocacy that trains them on how to speak knowledgeably about environmental sustainability, beef nutrition, animal welfare, and beef safety.
Comment
This is a great way to advertise beef, to associate beef with sports, and to deflect attention from the role of beef production in climate change, antibiotic overuse, and pollution of soil, air, and water. The checkoff program is a partnership with the USDA. Extremist Republicans want to get rid of checkoff programs (see Project 2025 agenda). So do I (politics does indeed make strange bedfellows).