A taste of summer: melons
Every now and then the USDA recruits a talented designer and produces terrific charts like this one.
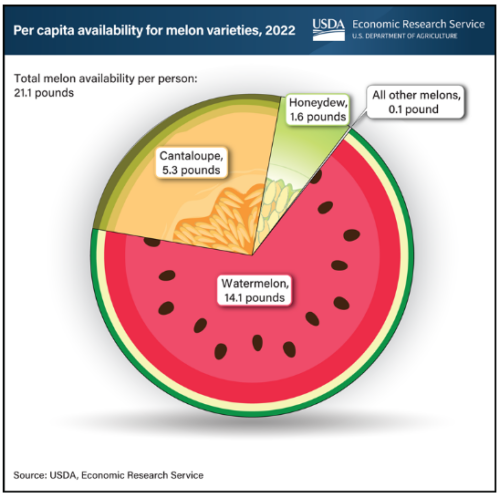
I thought this was perfect for a hot summer day. Enjoy!
Every now and then the USDA recruits a talented designer and produces terrific charts like this one.

I thought this was perfect for a hot summer day. Enjoy!
My distant (but dearly loved) cousin, the food package designer Michael Kravit, thought I would enjoy seeing this example of first-rate food marketing—and of a healthy product yet.

First, open the box.

Cut. Scoop. Enjoy!

You aren’t sure how? The company even supplies a video.
I’d like to see more like this.
Thanks to Bradley Flansbaum for sending this one from a journal not on my usual reading list: “In persons with constipation or IBS-C, kiwifruit vs. psyllium increased spontaneous bowel movements.”
I like the way this press release gets right to the point.
An industry-funded randomized trial assessed the effect of daily consumption of kiwifruit versus psyllium on GI function and comfort in 184 adults who were healthy, had functional constipation (FC), or met Rome III diagnostic criteria for constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C).
The study: Consumption of 2 Green Kiwifruits Daily Improves Constipation and Abdominal Comfort—Results of an International Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. The American Journal of Gastroenterology ():10.14309/ajg.0000000000002124, January 9, 2023. | DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002124.
Authors: Gearry, Richard MD, PhD; Fukudo, Shin MD, PhD; Barbara, Giovanni MD; Kuhn-Sherlock, Barbara PhD; Ansell, Juliet PhD; Blatchford, Paul PhD; Eady, Sarah MSc; Wallace, Alison PhD; Butts, Christine PhD; Cremon, Cesare MD; Barbaro, Maria Raffaella PhD; Pagano, Isabella MD; Okawa, Yohei PhD; Muratubaki, Tomohiko PhD; Okamoto, Tomoko PhD; Fuda, Mikiko MS; Endo, Yuka MD; Kano, Michiko MD, PhD; Kanazawa, Motoyori MD, PhD; Nakaya, Naoki PhD; Nakaya, Kumi PhD; Drummond, Lynley BTech (Hons)
Summary of the study
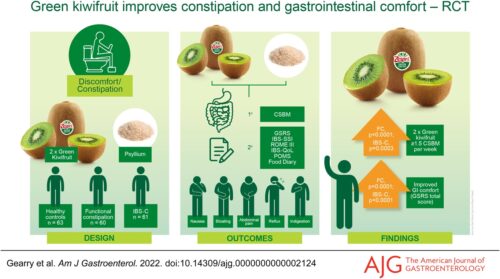
Methods: Participants included healthy controls (n = 63), patients with functional constipation (FC, n = 60), and patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C, n = 61) randomly assigned to consume 2 green kiwifruits or psyllium (7.5 g) per day for 4 weeks, followed by a 4-week washout, and then the other treatment for 4 weeks. The primary outcome was the number of complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBM) per week.
Results: Consumption of green kiwifruit was associated with a clinically relevant increase of ≥ 1.5 CSBM per week (FC; 1.53, P < 0.0001, IBS-C; 1.73, P = 0.0003) and significantly improved measures of GI comfort (GI symptom rating scale total score) in constipated participants (FC, P < 0.0001; IBS-C, P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: This study provides original evidence that the consumption of a fresh whole fruit has demonstrated clinically relevant increases in CSBM and improved measures of GI comfort in constipated populations. Green kiwifruits are a suitable dietary treatment for relief of constipation and associated GI comfort.
Financial support: Zespri International Ltd. was the principal sponsor and reviewed, approved, and funded the study design. The New Zealand study center trial was jointly funded by a grant from the New Zealand government (Contract C11X1312) and the sponsor company, Zespri International Ltd. In Italy and Japan, Zespri International Ltd. was the sole funder for each study center trial. The funder did not contribute to the study design or data analysis.
Potential competing interests: J.A. and P.B. are employed by Zespri International who part-funded the study. R.G. and L.D. sit on the Science Advisory Board, have received travel and research grants from Zespri International. SF and GB have received research travel grants from Zespri International.
Comment: Can you guess what Zespri International sells? Go on. Take a wild guess. I’ll admit it. I’d go for kiwi over psyllium every time. But we are talking here about an average improvement of 1.5 bowel movements a week, which may or may not be clinically meaningful.. I do give the authors credit for claiming a benefit for “fresh whole fruit,” not specifically kiwifruit. The study didn’t compare kiwi to other fruits (and why would it, given the kiwi fruit sponsor). But overall, this is yet another study done for marketing far more than scientific purposes.
NutraIngredients, a newsletter I read daily, caught my eye with this headline:
Blueberries benefit postmenopausal women with high blood pressure: Study: Daily blueberry consumption improves endothelial function in postmenopausal women with high blood pressure, according to a recent study…. Read more
I looked it up, of course.
Comment: Yes there is a conflict of interest, but the authors don’t seem to recognize it. This is a classic case of interpretation bias; the study didn’t show much of anything but the authors conclude that blueberry powder does some good.
High marks to NutraIngredients for disclosing the funding source right at the top of the article:
Published in the journal Food and Function, the study was supported by the US Highbush Blueberry Council and the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
*******
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.

It feels like spring (at last!) in New York so I’m thinking about strawberries.
Last September, Lisa Young sent me a copy of an email she had received from a public relations agency.
Good Morning –
Today is World Alzheimer’s Day and a new study has found that eating Strawberries may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and related dementias.
In fact, the compounds that give strawberries their beautiful red color may have several health benefits, such as lowering the risk of heart disease and some cancers and improving blood sugar control. And now researchers have found that one of those compounds, known as pelargonidin, may slow or prevent the development of Alzheimer’s Disease by lowering the number of twisted fibers inside the brain that contain a protein called tau. These twisted fibers are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s Disease.
The new study, which was supported by the National Institute of Aging and the California Strawberry Commission, was conducted postmortem on the brains of participants of the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP). Participants with the highest level of pelargonidin intake prior to their death also had less buildup in the brain of protein fragments called amyloid beta plaques – another hallmark of Alzheimers Disease. Pelargonidin is primarily found in berries. In this study, strawberries were the principal source of pelargonidin….
The study: Agarwal P, Holland TM, James BD, Cherian LJ, Aggarwal NT, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA. Pelargonidin and Berry Intake Association with Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology: A Community-Based Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;88(2):653-661. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215600. PMID: 35694918.
Results: “participants in the highest quartile of pelargonidin intake when compared to those in the lowest quartile, had less amyloid-β load (β (SE) = -0.293 (0.14), p = 0.038), and fewer phosphorylated tau tangles…”
Conclusion: “Higher intake of pelargonidin, a bioactive present in strawberries, is associated with less AD neuropathology, primarily phosphorylated tau tangles.”
Comment: I love strawberries and grow them in pots on my terrace. But this study? It looks at one chemical among many in strawberries and associates it with improved symptoms. Association, alas, does not indicate causation. If you give this a moment’s thought, could you believe that eating a few strawberries every day would help you prevent Alzheimer’s? I’m all for plant-based diets. And I’m all for eating strawberries. But to imply that strawberries alone can control hunger, be good for your heart, especially if they come from California (as the Commission says on its website), seems a bit much.
Are strawberries demonstrably better for Alzheimer’s than any other berry or fruit? The California Strawberry Commission is not interested in asking comparative questions. It just wants you to buy more strawberries.
*******
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.

Methods: This was a two-week controlled clinical trial to measure the effects of watermelon juice on responses to oral glucose challenge tests in healthy young adults. These usually decrease heart rate variability (not good).
Results: Watermelon juice countered the reduction in heart rate variability.
Funding: “This research was funded by the National Watermelon Promotional Board.”
Comment: I learned about this study from an article in NutraIngredients-USA: “Watermelon juice may decrease dysfunctsion linked to hyperglycemic episodes.” That headline made me ask my usual question: Who paid for this? Bingo.
I give NutraIngredients much credit for the funding reveal right after the first paragraph, and for its clear explanation of a complicated study rationale and design.
The authors say they have no conflicts of interest to declare. I continue to believe that the funding source establishes an automatic conflict of interest.
Once again, as I discuss in detail in my book, Unsavory Truth, the key point about industry-funded studies is that funding recipients do not recognize the influence or the conflict.
But what a coincidence that industry-funded studies so often come out with results favorable to the sponsor’s commercial interest, which in this case is this: The National Watermelon Promotional Board “operates with a single objective: to increase consumer demand for watermelon through promotion, research, and educational programs.”
Thanks to Larissa Zimberoff (“Technically Food”) for forwarding this gem of a press release.
Grape Consumption Helps Counter UV Damage to Skin
Recent study reinforces promising role of grapes in photoprotection
A recent human study published in the scientific journal Antioxidants found that consuming grapes protected against ultraviolet (UV) damage to the skin.[1] Study subjects showed increased resistance to sunburn after consuming 2 ¼ cups of grapes [sic] every day for two weeks. Additionally, subjects displaying UV resistance also demonstrated unique microbiomic and metabolomic profiles suggesting a correlation between the gut and skin. Natural components found in grapes known as polyphenols are thought to be responsible for these beneficial effects.
The title alone makes me ask: Who paid for this?
Here’s the study: [1] Pezzuto, J.M.; Dave, A.; Park, E.-J.; Beyoğlu, D.; Idle, J.R. Short-Term Grape Consumption Diminishes UV-Induced Skin Erythema. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122372
Funding: “This work was supported in part by the California Table Grape Commission (J.M.P and J.R.I./D.B.).” The funding statement continues:
The sponsor was not involved in the preparation of the article; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit this article for publication.
Comment: That’s what they all say, despite much overall evidence to the contrary.
Why the sic? The study was not, in fact, done wtih grapes., It was done with “whole grape powder – equivalent to 2.25 cups of grapes per day – for 14 days.”
Are powdered grapes the same as whole grapes? Would anyone be willing to eat 2.25 cups of whole grapes every day for 14 days?
I like grapes, and grow two kinds on a fence in Ithaca, some for eating, the Concord ones for jam. Grapes are fruit. Fruit is good for health. Eat them if you like them. They are useful parts of healthy diets.
Are grapes the only fruit that helps counter UV damage to skin? I doubt it. But I’m guessing sunscreens work better.
********
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.

The USDA’s Economic Research Service was damaged serriously when the Trump Administration moved its offices out of Washington DC to Kansas, and it is taking some time to recover.
It’s still publishing what it calls Charts of Note.
These are on all kinds of topics dealing with farm production and food consumption. Here are a couple of examples I found particularly interesting.
Here’s the first:
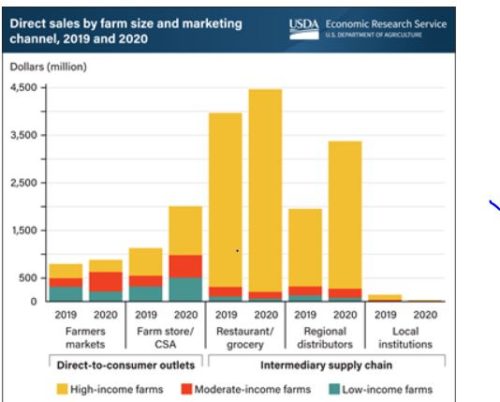
This one shows that small and medium size farms make money selling direct to consumers at farmers’ markets and via Community Supported Agriculture, but the largest farms benefit most from these opportunities. Restaurants and grocery stores don’t source much from smaller farms and neither do regional distributors.
The challenge for small and medium size farms is to find more and better distribution channels.\
And here’s the second:
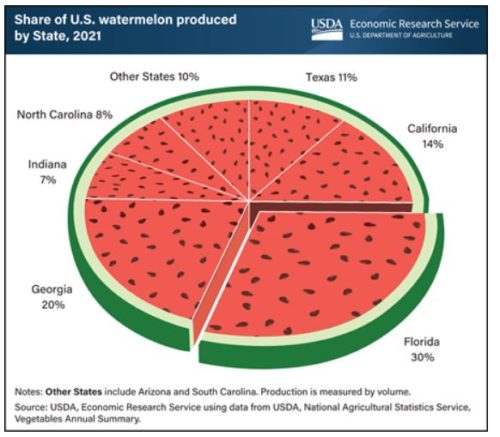
I picked this one because I like the design and because this watermelon has seeds. You can hardly buy a watermelon with seeds anymore.
I’ve been convinced that seedless watermelons don’t taste as good as the ones with seeds. This year, I bought some seeds from old-fashioned watermelon and planted them in my place in Ithaca, New York. They are now ripe, and edible. But alas: I don’t think they taste any better than the ones without seeds.
Next year, we plant seedless.
One big question: how do you get create seeds for seedless watermelons? This, I had to look up.
Seedless melons are referred to as triploid melons while ordinary seeded watermelons are called diploid melons, meaning, that a typical watermelon has 22 chromosomes (diploid) while a seedless watermelon has 33 chromosomes (triploid). To produce a seedless watermelon, a chemical process is used to double the number of chromosomes. So, 22 chromosomes are doubled to 44, called a tetraploid. Then, the pollen from a diploid is placed on the female flower of the plant with 44 chromosomes. The resulting seed has 33 chromosomes, a triploid or seedless watermelon. The seedless watermelon is sterile. The plant will bear fruit with translucent, nonviable seeds or “eggs.”
Aren’t you glad I asked?
************
Coming soon! My memoir coming out in October.
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.
