Sugar industry: here’s what we think about advice to eat less sugar
I am a faithful subscriber to Jerry Hagstrom’s Hagstrom Report on issues having to do with agriculture. He attended the International Sweetener Symposium in San Diego and took notes. If you want to know how the sugar industry is dealing with the “eat less sugar” message, here are some hints (wish I’d been there):
From José Orive, executive director of the London-based International Sugar Organization:
There is “sugar diarrhea” in the media, Orive said, referring to the many articles urging reductions in sweetener consumption. “We need to talk the bull by the horns in pointing out the role of sugar in human nutrition” and talking about the importance of exercise.
From Craig Ruffolo, an analyst with McKeany-Flavell in Oakland, CA:
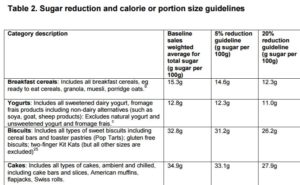
We need to get back to positivity, not negativity. The sugar industry has a really great message. It starts with 15 calories per teaspoon.
From Courtney Gaine, president and CEO of the Sugar Association:
“We have this obesity crisis that has become a massive economic problem,” Gaine said. The pressures on governments to address the human and economic costs of obesity have combined with “a public health community that does not trust industry” she said.
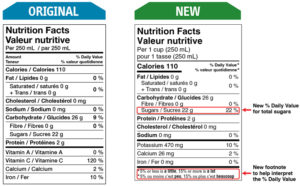
A lot of the food companies “who should be our friends” are instead reformulating products and advertising they are using less sugar, she said. Coca-Cola is replacing its “Coke Zero” with a label that reads “Coke No Sugar” and is already supplying Delta Air Lines with napkins bearing that slogan.
From Lynn Dornblaser, director of innovation and insight at Mintel, a Chicago market research firm:
“Products making low sugar claims won’t be going away anytime soon”…The “no high-fructose corn syrup” claim “is not losing its power.”
Hagstrom’s summary comes with references:
▪ American Sugar Alliance – “An Evaluation of the Global Sugar Market Environment” by José Orive
▪ “Sugar Market Outlook” by Craig Ruffolo
▪ “The New State of Play for Sugar: Trends, Policy, Consumption and Activism” by Courtney Gaine
▪ “Consumer Trends and Industry Response” by Ron Sterk
▪ “Trends in sugar, sugar reduction, and sweeteners” by Lynn Dornblaser