For those of us who have observed the Dietary Guidelines since they first came out in 1980, everything about them is a source of endless fascination, if not exhausting. They engender enormous fuss, but the basic dietary advice stays the same, year after year. It just gets presented in ways that are increasingly lengthy and complicated.
I have a vested interest in all this. I was a member of the 1995 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee.
Critics of the 2015 guidelines got Congress to order a review of the process by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), which produced two reports. The 2017 report recommended seven improvements to the process. Congress then mandated an evaluation of how well USDA and HHS had implemented the recommendations.
NASEM has just published the first of what will be two evaluation reports: Evaluating the Process to Develop the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025: A Midcourse Report. This one responds to the first of three questions and part of the second.
- Question #1: How did the process used to develop the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, compare to the seven recommendations included in the 2017 National Academies report?
- Question #2: Did the criteria used to include scientific studies used to inform the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, ensure that the evidence base was current, rigorous, and generalizable or applicable to public health nutrition guidance?
My reading of this report is that the agencies and their advisory committee did a pretty good job of producing the 2020-2025 guidelines, given the tight time schedule, the lack of resources, and the fundamental difficulties of producing solid evidence for the effects of diet on disease risk. The report’s conclusion (p. 106):
Finally, the committee identified many instances of partial implementation of the recommendations from the 2017 National Academies report. Some of these (e.g., recommendation 6) were minor concerns. Many other concerns that might, individually, seem minor represent a more substantial concern when considered together. For example, the many seemingly small deviations from committee-identified practices for systematic reviews together reduce the quality and utility of this important element of the evidence used to develop the DGA. Moreover, the combined effect of recommendations for which there were substantial concerns with those that were not implemented at all represents a continuing risk to the integrity of the DGA process.
The report, by the way, is 295 pages.
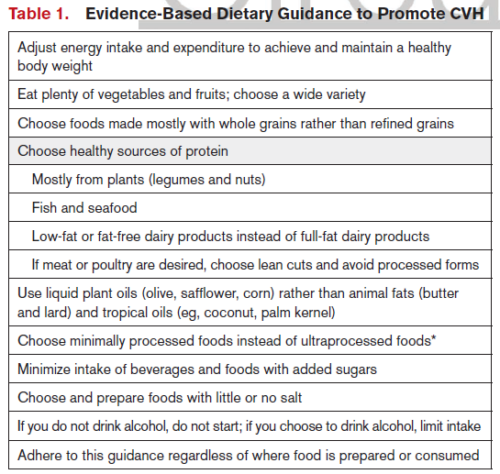
Do we really need all this? The guidelines stay pretty much the same from edition to edition: eat more fruits and vegetables (plant foods); don’t eat much salt, sugar, saturated fat; maintain healthy weight. Or, as Michael Pollan famously put it, “Eat food. Not too much. Mostly plants.”
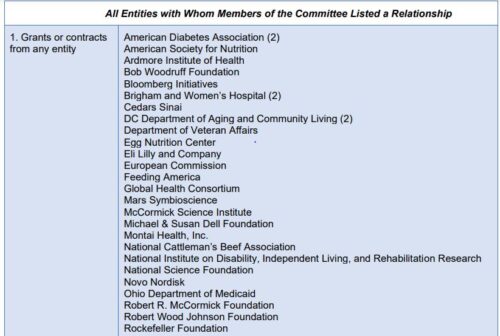
The food industry has the biggest stake in dietary guidelines, which is why we have to go through all this.
As I like to put it, I’ve made a career of criticizing dietary guidelines, and I’m not the only one. I’m ready to move on. If only.