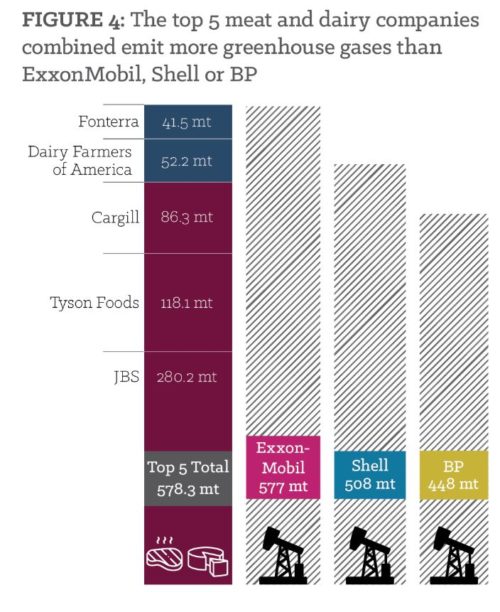
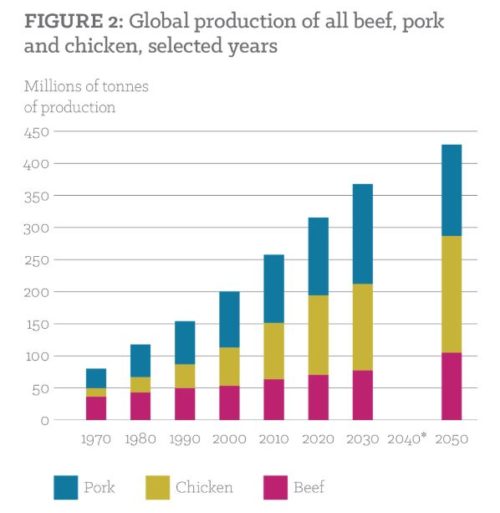
Halal meat: Global Meat News’ updates on the industry
Global Meat News is one of those industry newsletters I subscribe to. This is a collection of its articles on halal meats—those from animals slaughtered and prepared according to Muslim dietary laws.
The market for halal meats is increasing worldwide.

Global Meat News’ Special Edition: Halal
Halal produce is continuing to grow in demand across the international meat market, with China, Russia and Mexico showing a recent surge of interest in certifications and exploring opportunities for export. Is it time for halal meat to win over its previous critics by embracing the 21st century?
- Demand for halal meats to raise Mexican export market: Mexico is set to open up export opportunities for halal certification into the Muslim market… Read
- Russian meat giants drive up halal exports: Russia exported 50,000 tonnes (t) of halal meat in 2017, up almost twofold compared to 2016, as major agricultural holdings Cherkizovo, Miratorg and GAP Resource have shown increasing interest in this segment, according to the International Center for Halal Standardisation and Certification… Read
- Japan’s halal wagyu industry grows as Asian Muslim tourism increases: Japan’s halal wagyu industry is poised for rapid growth, thanks to demand from an increasing number of Muslim tourists and the opening of new export markets… Read
- Saudi regulatory board concerned over Brazilian chicken slaughter: Saudi Arabia’s regulatory board has expressed concerns about chicken products from Brazilian slaughterhouses and the need for investment from the Brazilian slaughterers to make improvements… Read
- Chinese company steps up halal beef production: A leading Chinese beef firm with overseas halal sales is opening a new plant this month that will double its capacity… Read
- Russia looks to export opportunity for halal venison: A recently opened slaughterhouse in northern Siberia has been certified to sell venison in accordance with Islamic standards (halal) and is currently in negotiations to export commercial batches of premium cuts to Iran and the United Arab Emirates (UAE)… Read
- Lisaili abattoir trials Al Mawashi smart app delivery service during Ramadan: The Dubai Municipality has trialled the Al Mawashi smart application at its Lisaili abattoir, for meat to be delivered to customers during Ramadan… Read
- Russia to promote halal poultry internationally: Around 75-80% of poultry that Russia plans to export in 2020 will be labelled as halal, according to Aidar Gazizov, director general for the International Center for Halal Standardization and Certification, speaking at the international summit Agroinvest Russia-2017 in Moscow… Read