The PCAST report: a timid step forward
PCAST, the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology, has released its REPORT TO THE PRESIDENT A Vision for Advancing Nutrition Science in the United States.
I learned about the report from a Tweet (X): 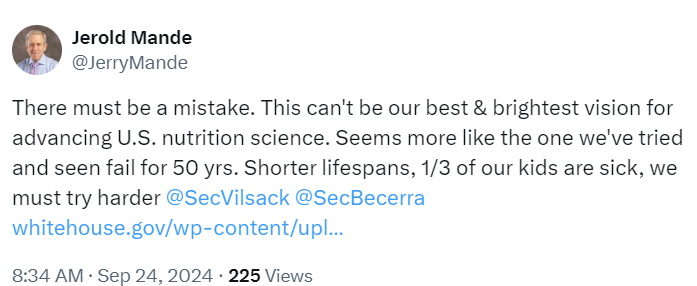
I wrote about an earlier draft of the report in a previous post: The federal vision for chronic disease prevention: individual behavior, not the environment. I called for the report to take on the need for fundamental improvements in the food environment aimed at preventing obesity-influenced chronic diseases.
If you read the fine print, the report has indeed done some of that. It now mentions ultra-processed foods, for example,
people’s food selections are complex, influenced by various factors in a multifaceted U.S. (and global) food ecosystem, with many of these factors beyond an individual’s control, e.g., increased production and availability of ultraprocessed foods which are associated with overconsumption and obesity. In addition to widespread availability of inexpensive ultra-processed foods, the U.S. food environment has undergone huge changes in recent decades, including easy access to low-cost fast food and eating away-from-home becoming much more common…in the era of widespread internet and digital technology access and use, people’s food habits increasingly are influenced by advertising and social media, which are sources of both facts and misinformation. Acknowledging and understanding these factors and their intersections is critical to addressing nutrition-related health disparities.
It also says useful things like these:
- new emphasis must be placed on nutrition research that can equitably and effectively help all Americans achieve better health.
- [needed is an] equity focus that particularly considers those who are disproportionately affected—racially, ethnically, and socially minoritized groups—due to long-standing and structural inequities which make it hard for many people to eat healthy and be physically active.
- For such a highly developed nation, the U.S. has distressingly high rates of food insecurity, imbalanced nutrition, and inequities in food access, all further exacerbated by the pandemic. With diet-related disease rates increasing, we have responded by focusing resources on costly medical treatments, further widening disparities and directing efforts away from prevention or addressing social determinants of health and a food environment that for too many Americans does not provide or promote good nutrition. The only way to reverse these trends and achieve robust health for our nation is to focus on prevention, which will require significant modifications of our overall food environment and must be informed by improved nutrition research.
- Preventing diet-related chronic diseases is among the most urgent public health challenges facing the nation.
Despite these statements, its two recommendations say nothing beyond the need for coordination aimed at addressing that challenge.
1. The Administration should implement a coordinated and sustained federal interagency effort, co-led by HHS and USDA, to strengthen the nutrition science base for current and future public and private sector actions to reduce the burden of diet-related chronic disease and maintain momentum toward the President’s 2030 goal.
2. To ensure equitable access to the benefits of nutrition research, federal agencies should prioritize equity in nutrition research, focus research on improving program delivery, continue efforts to diversify the nutrition science and dietetics workforce and engage the academic and private sectors in multisector research and intervention initiatives.
Yes, coordination would be a big help. Nutrition research is all over the place at the federal level. So would increased funding for nutrition research aimed at improving the food environment to prevent chronic disease. Only a tiny fraction of the NIH budget goes for this purpose. NIH’s main nutrition focus is “precision nutrition” aimed at individuals, not public health. And much of the USDA’s nutrition funding goes to the kinds of industry-funded studies I post here on Mondays.
The report mentions what’s needed in theory; it ducks dealing with the tough politics of chronic disease prevention.
And alas, it did not cite my suggestions for what is needed (which I had sent to the committee).
So where is leadership for chronic disease prevention at the federal level? It’s in an odd place at the moment, as I will discuss tomorrow.