Dietary guidelines I. Ultra-processed foods
I don’t like writing about the dietary guidelines process while it is still ongoing because so much can change between now and the time the advisory committee submits its report, and USDA and HHS issue the actual guidelines.
But this Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee is dealing with the concept of ultra-processed foods and is tied in knots over it.
So I will devote this week to the guidelines.
- Today: Why knots?
- Wednesday: Why isn’t NIH funding more rigorous nutrition research?
- Thursday: Why all the fuss when guidelines always say the same things?
OK. Let’s get to it.
Why do I think the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) is tied in knots over ultra-processed foods (UPF)?
- It is required to make evidence-based recommendations. This is impossible with observational evidence.
- It is required to exclude the one existing controlled clinical trial from consideration (because it was too short).
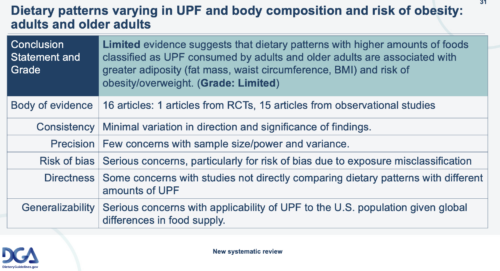
Therefore, it had to conclude: ““Limited evidence suggests that dietary patterns with higher amounts of foods classified as UPF consumed by adults and older adults are associated with greater adiposity (fat mass, waist circumference, BMI) and risk of obesity/overweight. Evidence Grade: Limited.”
The DGAC is in an impossible position, and doing the best it can under the circumstances.
I need to say a word about evidence-based recommendations. How I wish they could be. If all you have is observational studies, you need to interpret them carefully. Interpretation is subject to bias.
When I was a DGAC member (1995 guidelines), the agencies recognized what we were up against. They instructed us to review the available research and give the best advice we possibly could based on it.
All of this raises a philosophical question: Should government agencies issue advice based on incomplete and inadequately controlled observational research? Or should they say nothing?
This committee, apparently, is considering saying nothing about ultra-processed foods: “It would be hugely problematic to tell people to avoid 60% of the food supply without having something good to replace it.”
Really? Plenty of “something good” is available. It’s called food: fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, fish, dairy, eggs.
These—unprocessed and minimally processred—can be delicious, nutritious, and satisfying, and at reasonable cost.
—–
Tomorrow: Why don’t we have more rigorous research?
Addition: The video of the meeting. The discussion of ultra-processed foods starts at 3:51:45 .