Summary box
-
In the modern, globalised food system, useful types of industrial food processing that preserve foods, enhance their sensory properties and make their culinary preparation easier and more diverse, have been and are being replaced by food ultra-processing.
-
The main purpose of food ultra-processing is to increase profits by creating hyperpalatable and convenient food products that are grossly inferior imitations of minimally processed foods and freshly prepared dishes and meals.
-
In the last decades, obesity, type 2 diabetes and related diseases have become global epidemics, leading the health systems of many countries to or beyond breaking point.
-
Taken together, the totality of evidence summarised here shows beyond reasonable doubt that increased consumption of ultra-processed foods is a major contributor to the pandemic of obesity, type 2 diabetes and related diseases.
-
The 2021 UN Food System has a unique opportunity to urge countries to implement policy interventions required to reduce ultra-processed food production, distribution and consumption, while simultaneously making fresh or minimally processed foods more available, accessible and affordable.
Introduction
The UN Food Systems Summit is taking place later this year at a crucial time. Food systems are manifestly failing to enhance human health, social equity or environmental protection. One symptom is the pandemic of obesity and related non-communicable diseases with their vast consequences. As we show here, one of the main drivers of this pandemic is the transformation in food processing. In the modern, globalised food system, useful types of food processing that preserve foods, enhance their sensory properties and make their culinary preparation easier and more diverse, have been and are being replaced by deleterious types of processing whose main purpose is to increase profits by creating hyperpalatable and convenient products that are grossly inferior imitations of minimally processed foods and freshly prepared dishes and meals. The Summit has a unique opportunity to confront this calamitous change, and to recommend effective policies and actions to UN agencies and member states.
Processing and industry
The key issue here is the nature, purpose and extent of food processing. It is not processing as such. General criticism of food processing is too unspecific to be helpful. Most foods are processed in some way, and culinary preparations of fresh foods are usually made using processed ingredients. Some types of food processing contribute to healthful diets, but others do the opposite.1
At one extreme are minimal processes which mostly preserve or enhance whole foods, such as drying grains, pulses and nuts, grinding grains into flour and pasta, chilling or freezing fruits and vegetables, pasteurising milk and fermenting milk into yoghurt.
At the other extreme are industrial processes that convert food commodities such as wheat, soy, corn, oils and sugar, into chemically or physically transformed food substances, formulated with various classes of additives into generally cheap to make, long duration substitutes to minimally processed foods and freshly prepared dishes and meals. The result is brand-named sugary, fatty and/or salty food and drink products which typically contain little or no whole food, are designed to be ready-to-consume anytime, anywhere and are highly attractive to the senses or even quasi-addictive. These products, including sweet and flavoured drinks, sweet or savoury snacks, reconstituted meat products and shelf-stable or frozen ready meals and desserts, are identified as ultra-processed foods.2
Criticisms of the food industry as a whole are also a mistake. Most of the very many millions of food farming, growing, rearing, making, distributing, selling and catering businesses throughout the world, notably in Asia, Africa and Latin America, deal solely or largely in fresh and minimally processed foods. These businesses and the foods they produce need to be encouraged, defended and supported.
By contrast, ultra-processed foods are mostly enabled, produced and sold by a small number of transnational corporations, some of whose turnovers exceed the revenues of many countries and make annual profits of US$ billions.3 These corporations use their power to formulate, mass manufacture, distribute and aggressively market their products worldwide.4
These corporations shape scientific findings by funding in-house and university-based research, so as to defend and promote ultra-processed foods.5 They also exercise political power by intensive lobbying, donations and sponsorships, and until now have dissuaded most governments from adequately regulating their products and practices.6
Time-series food sales data indicate the explosive growth in manufacturing and consumption of ultra-processed foods worldwide.7 National dietary surveys show that ultra-processed foods already make up 50% or more of total dietary energy intake8 in high-income countries, with even higher consumption among children and adolescents.9 In middle-income countries, they now represent between 15% and 30% of total energy intake8 but sales of ultra-processed foods are increasing fastest in these countries.10
The pandemic of obesity and related diseases and its link with ultra-processing
According to WHO, worldwide prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since the mid-1970s, and now over 650 million adults are obese, and 1.9 billion adults and over 370 million children and adolescents are overweight or obese (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight). No country has yet reversed these increases. Closely driven by the increase in obesity is a doubling of worldwide type 2 diabetes prevalence since 1980, now affecting about 420 million people (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes). Obesity, type 2 diabetes and related non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and some common cancers, have become pandemics. Pre-COVID-19, health systems in most countries did not have the capacity to effectively treat diet-influenced diseases. Now, many health systems are at or beyond breaking point struggling with COVID-19, the severity of which is significantly higher in people with obesity and related diseases.
Evidence of the general healthfulness of dietary patterns based on fresh and minimally processed foods and culinary preparations, and their protection against all forms of malnutrition, ‘is noteworthy for its breadth, depth, diversity of methods, and consistency of findings’.11
But only in the last decade, with the advent of the NOVA food classification system that distinguishes ultra-processed foods from minimally processed or processed foods,1 has the link between changes in types of food processing and the pandemic of obesity and related diseases been revealed. Evidence here includes:
-
Three meta-analyses of findings from epidemiological studies, including large, long-duration, carefully conducted cohort studies, show dose-response associations between consumption of ultra-processed foods and obesity, abdominal obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidaemias, metabolic syndrome, depression, cardio and cerebrovascular diseases and all-cause mortality.12–14
-
Analysis of national dietary or food purchase surveys in middle-income or high-income countries shows that the higher the dietary share of ultra-processed foods, the higher the obesogenic dietary nutrient profiles. These are characterised by higher energy density, free sugars, unhealthy fats and sodium, and lower protein and dietary fibre.8
-
Epidemiological and experimental studies indicate that ultra-processed foods may increase risks for obesity and related diseases in other ways beyond their nutritional composition. These include structural and physical properties that blunt satiety signalling, organoleptic characteristics associated with higher energy intake rate, neo-formed substances and migrated packaging materials that are endocrine disruptors, additives that promote pro-inflammatory microbiome, and reduced thermic effect that decreases total energy expenditures.12–14
-
A randomised controlled cross-over trial shows that consuming a high ultra-processed diet causes a highly significant increase in ad libitum calorie intake and consequent weight gain. Over a 2-week period, 20 young adults following a diet with 83% of energy from ultra-processed foods consumed approximately 500 more kcal per day than when they followed a diet with no ultra-processed foods. Participants gained 0.9 kg at the end of the 2 weeks with the ultra-processed diet and lost 0.9 kg at the end of the non ultra-processed diet, mostly of body fat.15
-
A longitudinal ecological study of 80 countries from 2002 to 2016 shows a direct association between changes in annual per capita volume sales of ultra-processed foods and corresponding changes in population adult body mass index.16
Taken together, the totality of evidence summarised here shows beyond reasonable doubt that increased consumption of ultra-processed foods is a major contributor to the pandemic of obesity and related diseases. There is also mounting evidence of the harmful effects of the ultra-processed food industry on the planet, through its global demand for cheap ingredients that destroy forests and savannah, its displacement of sustainable farming, and its resource-intensive manufacturing and packaging.17
Policy responses
To begin with, the UN Food Systems Summit should urge international and national health and food and nutrition authorities to review their dietary guidelines to emphasise preference for fresh or minimally processed foods and avoidance of ultra-processed foods, in line with guidelines developed, for example, by the WHO/Pan American Health Organization,18 and issued in several Latino-American countries, and now also in France, Belgium, and Israel.
At the same time, national governments should be urged to use fiscal measures, marketing regulations, bold mandatory front-of-pack labelling schemes and food procurement policies, all designed to promote the production, accessibility and consumption of a rich variety of fresh or minimally processed foods, and to discourage the production, distribution and consumption of ultra-processed foods, as now done in several countries.19
Current food and nutrition policies are mostly intended to encourage food manufacturers to reformulate their products by reducing the use of salt, sugar or unhealthy fats. There is a role for strong regulations that effectively limit the levels of these components, but reformulation alone will not turn ultra-processed products into healthy foods,20 as in effect recently acknowledged in one internal document from one leading ultra-processed food corporation – “some of our categories and products will never be ‘healthy’ no matter how much we renovate” (https://www.ft.com/content/4c98d410-38b1-4be8-95b2-d029e054f492). Policies should instead stimulate the entire manufacturing industry to maintain, develop or improve processing methods that prolong the duration of whole foods, enhance their sensory properties and make their culinary preparation easier and more diverse. Ultra-processed foods should be replaced by processed foods with limited levels or absence of added salt, sugar or unhealthy fats or, preferably, by minimally processed foods.20
Conclusions
Food systems are failing. This is most clearly shown by what are now the pandemics of obesity and type 2 diabetes, of which ultra-processed food is a main contributor. The UN Food Systems Summit should urge member states to implement multiple policy interventions to reduce ultra-processed food production, distribution and consumption, while simultaneously making fresh or minimally processed foods more available, accessible and affordable.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not required.
Acknowledgments
This paper expands a one-page submission made by the authors to the UN Food Systems Summit within Solution Cluster 2.2.1 (food environment).


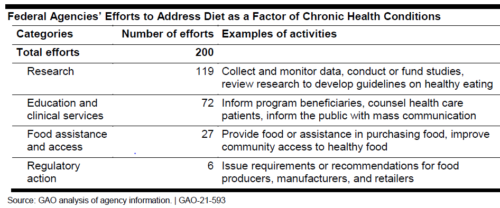 Most of these are focused on research.
Most of these are focused on research.