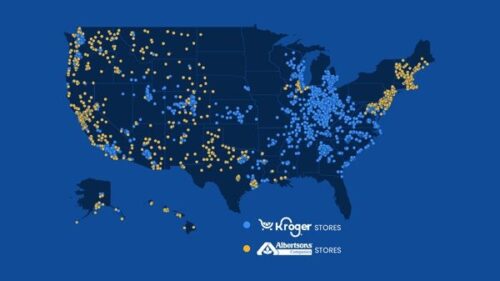
Good news: The Kroger-Albertson’s acquisition is not going to happen
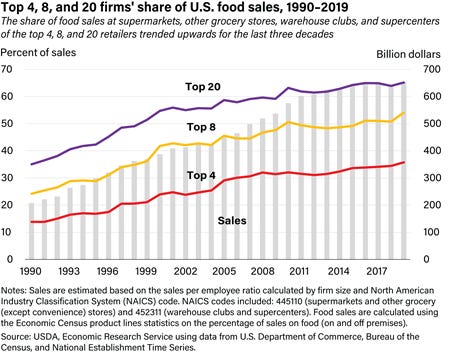
A federal judge has said no to the proposed $25 billion purchase of Albertson’s by Kroger. This is a win for the Federal Trade Commission and for consumers faced with store closures and higher prices almost certainly expected as a result of the merger.
U.S. District Judge Adrienne Nelson agreed in the ruling that the merger was likely to remove direct competition between the two grocers, which would make it unlawful…Albertsons shares were down around 2.2% on Tuesday afternoon. Kroger shares were up around 5%.
I’ve written about the proposed merger in earlier posts.
- Kroger v. the Federal Trade Commission: Not a pretty story
- The proposed Kroger-Albertson’s merger: divestment consequences
- Kroger’s acquisition of Albertsons: What this means
A lot of money was at stake. Now things are geting really ugly.
Albertson’s is suing Kroger for not trying hard enough to get the merger through the FTC.
Kroger says this charge is baseless.
“This is clearly an attempt to deflect responsibility following Kroger’s written notification of Albertsons’ multiple breaches of the agreement, and to seek payment of the merger’s break fee, to which they are not entitled.
The cases are likely to go on and on. In the meantime, enjoy going to your local supermarket while you can.