Kroger v. the Federal Trade Commission: Not a pretty story
Recall that the large grocery chain, Kroger, proposed a couple of years ago to acquire another large grocer, Albertsons, for about $25 billion.
The FTC did not think this was a good idea. It FTC filed a suit to prevent the proposed merger on the grounds that it would make the US supermarket landscape even less competitive than it already is. It would be likely to raise prices for consumers, reduce wages for employees, and (as I’ve written previously) lead to the closure of many stores.
Kroger is fighting back. It filed an injunction arguing that blocking the merger violates the constitution.
In its news release, Kroger said
“The merger between Kroger and Albertson’s is squarely focused on ensuring we bring customers lower prices starting day one while securing the future of good-paying union jobs,” said Rodney McMullen, Kroger Chairman and CEO. “We stand prepared to defend this merger in the upcoming trial in federal court – the appropriate venue for this matter to be heard – and we are asking the Court to halt what amounts to an unlawful proceeding before the FTC’s own in-house tribunal.”
In the meantime, BIG, a newsletter on the politics of monopoly power, reports
After two years of investigations and negotiations over court logistics, next week, the Federal trial for the $24 billion Kroger-Albertsons supermarket merger begins. And this one’s really bitter, with new revelations emerging a few days ago from the Federal Trade Commission that a group of Albertsons executives, including CEO Vivek Sankaran, have been deleting text messages relevant to the trial that the court ordered them to preserve. That’s a big legal no-no.
A big legal no-no indeed. This from the FTC’s complaint (references omitted)
On January 17, 2024, the FTC requested a detailed accounting from Albertsons about how responsive documents were lost and what efforts had been taken to recover lost documents. Albertsons did not respond for nearly four months. When they finally responded, they detailed efforts to recover deleted messages from Mr. Broderick’s and Vivek Sankaran’s phones. . Although Albertsons was able to recover approximately 70 text messages from Mr. Sankaran’s phone, further efforts proved unsuccessful…For months, Plaintiffs have tried to seek information about the extent to which Albertsons’ text messages were deleted, obtaining a court order in the Administrative Adjudication requiring production of texts from potential trial witnesses, and raising repeated inquiries about inexplicably missing documents.
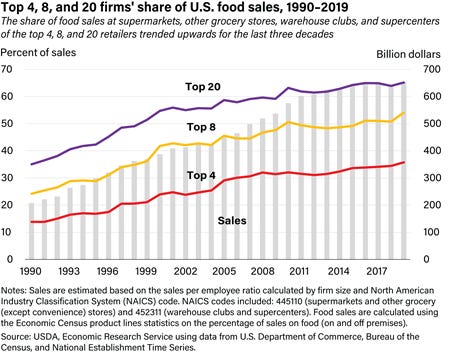
This is what the USDA says consolidation in the grocery industry looks like now. The proposed merger will only add to monopoly power int he grocery industry. For the record, Walmart accounts for about 25% of grocery sales int he US.
Is the Kroger-Albertson’s merger likely to be good for the public? The FTC does not think so and neither do I.