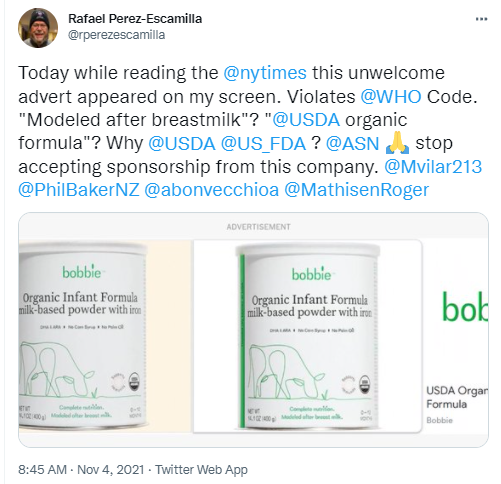
Infant formula marketing: an update
As the WHO/UNICEF report I posted yesterday makes clear, the marketing of infant formula—impossible for new mothers to avoid—interferes with breast feeding and, therefore, is a public health concern.
I posted about the Abbott Labs infant formula recall last week.
Here are some additional items I’ve collected on this topic.
I. What the marketing looks like.
II. Study finds no benefit of enriched infant formula on later academic performance: Children who are given nutrient or supplement enriched formula milk as babies do not appear to have higher exam scores as adolescents than those fed with standard formula, suggests a study published by The BMJ, leading researchers to argue renewed regulation is needed to better control infant formula promotional claims…. Read more
III. IBFAN, the International Baby Foods Action Network, writes that it is:
launching a PETITION calling for an immediate halt to a new study – funded by the Gates Foundation and led by researchers from the University of California – that is randomly allocating infant formula to breastfeed in low-birth-weight babies in Uganda and Guinea-Bissau on assumption that this might prevent wasting and stunting.
The study, which has been cleared by ethics committees in the USA, Uganda and Guinea -Bissau – uses purchased ready-to-use infant formula made by Abbott, a US pharmaceutical corporation operating in 160 countries. Abbott is a major violator of the International Code and is currently at the centre of a media storm in the USA because of contamination in its powdered formula. (NB. The formula used in the trial is liquid Ready-to-Feed).
IV. IBFAN issued an earlier statement: The baby food industry’s destruction of an irreplaceable natural resource.
The International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Substitutes was adopted forty years ago by the World Health Assembly, the world’s highest health policy setting body…Today 70% of countries have adopted laws based on the Code, however far too many are limited in scope and full of loopholes as a result of industry interference. As a consequence predatory marketing of baby food products continues throughout the world. and the global Baby Food Drink Market is forecast to rise more than 30% in 5 years (from $68bn in 2020 to $91.5bn by 2026)….Aside from its crucial role in child survival (more than 800,000 children die each year because they are not breastfed and many more do not reach their full potential, breastfeeding is the most environmentally friendly way to feed an infant, resulting in zero waste, minimal greenhouse gases, and negligible water footprint. As a renewable natural food resource, mother’s milk makes an important contribution to local food and water security.…the baby food industry lost no time in exploiting the fear and confusion during the pandemic: falsely claiming their products build immunity; that their ‘donations’ are humanitarian; encouraging the needless separation of mothers and babies and pretending that they are essential ‘partners’ who are genuinely working to address the problems.
V. The Access to Nutrition Initiative (ATNI) assesses nine formula companies’ adherence to WHO recommendations. Its report is here.
According to its press release,
Despite the World Health Assembly (WHA) adopting ‘The International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes’ forty years ago and passing 18 associated resolutions since (collectively referred to as ‘The Code’), the BMS/CF Marketing Index 2021 found that none of the companies it assessed fully abides by The Code’s recommendations and most fall well short.
The summary:
- Danone retained first place with a score of 68%, up from its 2018 score of 46%
- Nestlé, the market leader in sales value, retained its second place with a score of 57% – also a substantial improvement on its score of 45% in 2018
- KraftHeinz achieved the greatest improvement, ranking third, with a score of 38% compared to in 2018 when it didn’t score at all
- Reckitt (previously RB) substantially improved its BMS Marketing policies which led to a big jump in its score from 10% in 2018 to 32% in 2021 and climbing one place to fourth in the ranking.
VI. A study: Conflicts of interest are harming maternal and child health: time for scientific journals to end relationships with manufacturers of breast-milk substitutes. Pereira-Kotze C, et al. BMJ Global Health. 2022 Feb;7(2):e008002. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-008002
The promotion and support of breastfeeding globally is thwarted by the USD $57 billion (and growing) formula industry that engages in overt and covert advertising and promotion as well as extensive political activity to foster policy environments conducive to market growth. This includes health professional financing and engagement through courses, e-learning platforms, sponsorship of conferences and health professional associations and advertising in medical/health journals…journal publishers may consciously, or unconsciously, favour corporations in ways that undermine scientific integrity and editorial independence—even perceived conflicts of interest may tarnish the reputation of scientists, organisations or corporations. Such conflicts have plagued infant and young child nutrition science for decades.
Comment: As I mentioned yesterday, we now have more than enough evidence to put a stop to this.