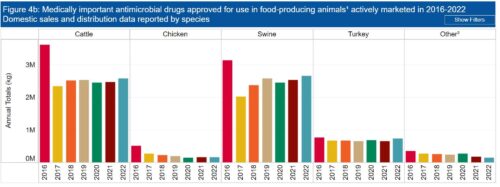
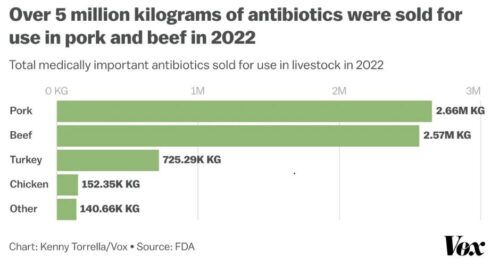
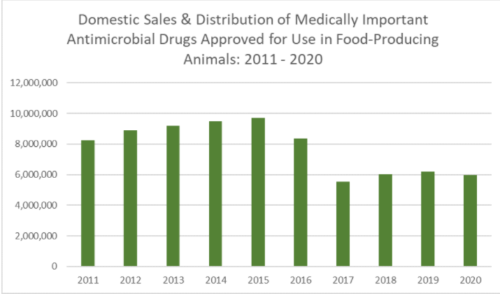
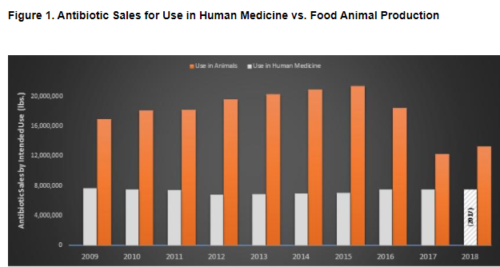
IPES-Food, the International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems, has a new report: The politics of protein: Examining claims about livestock, fish, “alternative proteins” and sustainability

The report contains a deep analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of these eight claims.
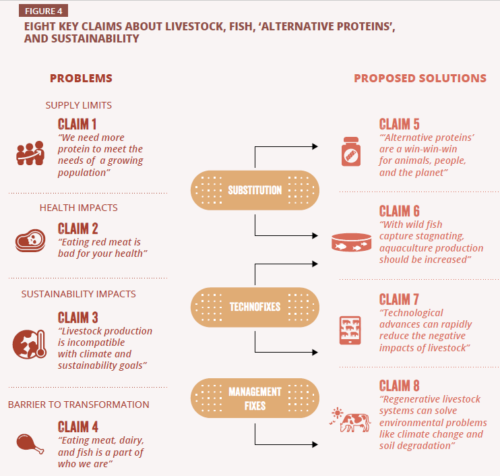
The report’s argument is that the focus on protein is overblown.
For decades, the perceived need for more protein has led to distractions and distortions in development programs, flawed marketing and nutritional campaigns, and calls to increase the production and trade of meat, dairy, and protein-enriched foods.
Today, the evidence clearly shows that there is no global ‘protein gap’: protein is only one of many nutrients missing in the diets of those suffering from hunger and malnutrition, and insufficiency of these diets is primarily a result of poverty and access.
The report displays data to back up its arguments in attractive and easily understood charts. Its conclusions are clearly marked. Example: part of the conclusion for Claim #5: Alternative proteins are a win-win.
In conclusion, there are too many uncertainties and data gaps, and too much variation between systems, to make a definitive statement on whether ‘alternative proteins’ are more environmentally sustainable than animal source foods as a whole. Bold and categorical claims about ‘alternative proteins’ being a ‘win-win-win’ are therefore likely to be misleading…The validity of claims about ‘alternative proteins’ (and the purported benefits of these products) ultimately comes down to how foods are produced, what food systems we consider to be desirable and viable, how we weigh up trade-offs ….
Sensibly, the report makes only three recommendations:

Comment: I think this report is well done, well written, and well presented. But here’s where this nutritionist gets cranky: Why title it Protein? Protein is a nutrient, not a food. Using protein to stand for foods that contain it is an example of “nutritionism,” the reduction of the benefits of a food to its single components.
I had to search the report for an explanation of what IPES means by protein. As far as I can tell, its writers assume you know what it means. But sometimes the report refers to meat and protein, implying that meat means beef, and protein means protein-containing animal foods other than beef. At other times, the report uses protein to include beef as well as poultry, fish, dairy, and insects. But what about vegetables and grains? They have protein too. Legumes are particularly good sources; grains have nourished entire civilizations.
I realize that protein—a chefs’ term—is widely understood to stand for all foods, particularly from animals, that contain protein, but that’s nutritionally incorrect because basically every naturally occurring food contains some protein (OK, lettuce doeesn’t have much).
I wish everyone would find a better term, one that calls meat meat, if that’s what’s meant.