Sunday viewing: Super Bowl food ads
Question of the day: What does a 30-second Super Bowl ad cost?
Answer: roughly $7 million (I’m not kidding—for 30 seconds).
Here is Statistica’s “Average cost of a 30-second Super Bowl TV commercial in the United States from 2002 to 2023.”
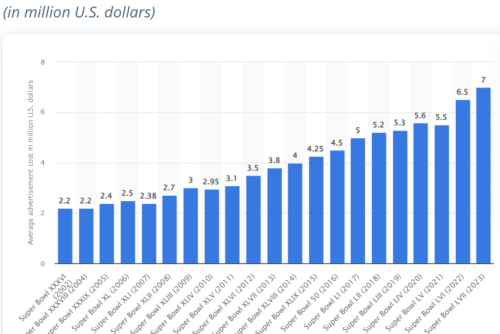
I have to confess to not being much of a football fan but I am riveted by the junk food content—and astronomical cost—of Super Bowl ads.
I first learned about this year’s collection from FoodNavigator—USA.
Super Bowl LVIII: The products, ads expected to make big plays during game dayWith the Super Bowl two weeks away, consumers are preparing their grocery lists and budgets for the big game day, as CPG brands ready their ads and promotions with the anticipation of receiving a volume boost the week after the game…. Read more
Here’s its prediction:
When it comes to what consumers will bring to Super Bowl parties, 72% said they will buy chips and dips, 44% pizza, 42% homemade appetizers, 35% side, and 33% pre-made appetizers.
Lesser purchased food items include fruit at 32%, cheese/charcuterie at 27%, and homemade desserts at 27%. Only 6% of consumers said they would bring nothing to a party.
Additionally, 47% of consumers said they are planning on purchasing alcoholic beverages, compared to 27% who said the same for non-alcoholic beverages.
However, 34% of shoppers under the age of 35, a demographic increasingly embracing a sober or sober-curious lifestyle, will be buying alcohol, compared to 72% of the consumers aged 55-64.
OK. The Super Bowl is an occasion for junk food and alcohol. Would you believe 1.45 billion chicken wings expected to be consumed during the game?
Brand Innovator lists the advertisers. Here are some of the food and alcohol advertisers:
- Budweiser, Bud Light, and Michelob ULTRA
- Hellman’s Mayonnaise
- Pringles
- Doritos
- Reese’s
- Frito-Lay
- Nerds
- M&Ms
- Coors Light
- Popeyes
- Drumstick
- DraftKinds
- Starry
- Mountain Dew Baja Blast
- Oreo
- Molson Coors
Here are some summaries:
- The dairy ads
- The beverage ads
Enjoy the game, but watch those calories!
Addition: a reader sent this SuperBowl infographic with much more on its being the #2 eating occasion (after Thanksgiving).










 I’m not sure how to interpret the “except” phrase, except that our FDA must think that the health claims on a product like this are entirely acceptable, whereas they would not be allowed in many other countries. [Reference 23 refers to UN General Assembly Resolution 63.23.]
I’m not sure how to interpret the “except” phrase, except that our FDA must think that the health claims on a product like this are entirely acceptable, whereas they would not be allowed in many other countries. [Reference 23 refers to UN General Assembly Resolution 63.23.]

