Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Captured by Food Corporations
The advocacy group, U.S. Right to Know, sent out a press release to announce publication of an article in the British journal, Public Health Nutrition: The corporate capture of the nutrition profession in the USA: the case of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics [AND, formerly the American Dietetic Association] accepted millions of dollars from food, pharmaceutical and agribusiness companies, had policies to provide favors in return, and invested in ultra-processed food company stocks, according to a study published today in Public Health Nutrition…The study was produced by public health scholars and U.S. Right to Know, a nonprofit investigative public health group that obtained tens of thousands of pages of internal Academy documents through state public records requests.
I’ve been writing about corporate capture of AND (formerly the American Dietetic Association) for years (see below), but this study shocked even me, for two reasons.
- AND holds stock in food companies making ultra-processed foods.
The documents show that the Academy and its foundation invested funds in ultra-processed food companies. The Academy’s investment portfolio in January 2015 included $244,036 in stock holdings in Nestle S.A. and $139,545 in PepsiCo. The Academy foundation’s investment portfolio in June 2013 included $209,472 in stock holdings in Nestle S.A and $125,682 in PepsiCo.
- The list of food companies donating to AND is extraordinarily long; it goes on for pages.
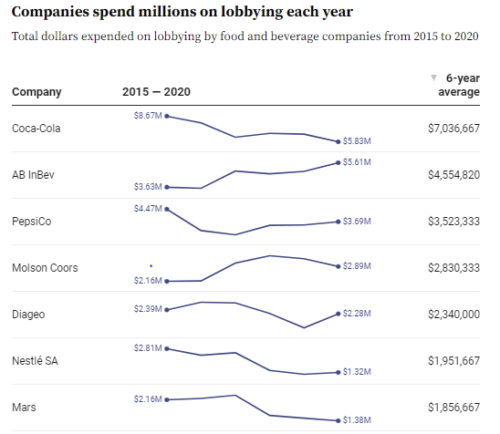
The Academy accepted more than $15 million from corporate and organizational contributors in the years 2011 and 2013-2017. The Academy’s top contributors in 2011 and 2013-2017 were:
- National Dairy Council $1,496,912
- Conagra Inc. $1,414,058
- Abbott Nutrition $1,246,389
- Abbott Laboratories $824,110
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Foundation: $801,261
- PepsiCo Inc. $486,335
- Coca-Cola Co. $477,577
- Hershey Co. $368,032
- General Mills Inc. $309,733
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality $296,495
- Aramark Co. $293,051
- Unilever Best Foods $276,791
- Kellogg USA $273,272
The Academy’s response: Inaccuracies in U.S. Right to Know Article
The report is disjointed, mostly opinion, emails taken out of context, picking and choosing items based on words out of Board reports, etc.
The Academy lists facts
- One of the authors has strong financial ties to CrossFit, a staunch opponent to RDN licensure.
- Less than 9% (12 out of 149) of named scholarships, awards and named research grants were established through industry. The funds that are established have input into scholarship criteria, which are approved by the Foundation’s Board. An independent review committee then reviews applications and selects recipients.
- Less than 2% (32 out of 2,812) of donors to the Academy’s Second Century were industry donors.
Additional Academy facts
- Fact: The Academy is NOT influenced by sponsorship money
- Fact: Less than 3% of the Academy’s and the Foundation’s investments are in food companies.
- Fact: The Academy has never changed a position at the request of sponsors.
- Fact: Less than 9% of Academy funding comes from sponsorship.
- Fact: The Foundation’s Fellows program allows participants to serve as catalysts for change and advancement in emerging areas of need for the evolving nutrition and dietetics profession.
- Fact: The Academy and Foundation have always been committed to accountability through transparency and fiduciary responsibility.
Comment
I have been writing about the Academy’s ties with food companies for years. See, for example,
- March 17, 2008 OK. Time to talk about the American Dietetic Association’s alliances with food companies
- March 13, 2015 Dietitians put seal on Kraft Singles (you can’t make this stuff up)
- March 18, 2015 Dietitians in turmoil over conflicts of interest: it’s about time
- March 1, 2017 The recent Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics’ election: controversy over non-disclosure of industry ties
- September 9, 2020 Dietetic Association lets Bayer, owner of glyphosate, educate its members about pesticides (but see correction below)
- A chapter in my book, Unsavory Truth: How the Food Industry Skews the Science of What We Eat
In my book, I document how food companies exert influence through sponsorship of research and professional societies. Typically, recipients of industry funding do not recognize the influence of sponsorship and deny it, as we see here.
If AND wants to be taken seriously as an organization devoted to public health, it needs to set strong guidelines for conflicts of interest and adhere to them. At the moment, this organization gives the appearance of a public relations arm of the food industry.
The same can be said of the American Society of Nutrition, but that’s another story.
Resources
- U.S. Right to Know publishes a fact sheet on AND: available here.
- MedPage: Nutrition Group Has Close Ties to Food, Pharma Companies —
- Washington Post: Group shaping nutrition policy earned millions from junk food makers (I’m quoted in this)
***********
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.