Food companies interested in doing something meaningful to prevent childhood obesity are in a bind. Preventing obesity usually means staying active; eating real, not processed, foods; and reserving soft drinks and juice drinks for special occasions. None of this is good for the processed food business. At best, food and beverage companies can make their products a bit less junky and back off from marketing to children. In return, they can use the small changes they make for marketing purposes.
Perhaps as a result of Michelle Obama’s campaign (see yesterday’s post), companies are falling all over themselves – and with much fanfare – to tweak their products.
GROCERY MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION (GMA): By all reports, GMA members applauded Mrs. Obama’s remarks. GMA says its member companies are already doing what she asked.
Parke Wilde, a professor at the Tufts School of Nutrition (and food policy blogger), gave a talk at that meeting in a session dismissingly titled, “The New Foodism.” His comment:
I enjoyed hearing Michelle Obama’s talk, which was well written and delivered and fairly forceful in places. In my afternoon panel, I said grocery manufacturers would find some threatening themes in books and documentaries promoting local and organic and sustainable food, but that there is also much of substance and value. Then, Susan Borra [Edelman Public Relations] and Sally Squires [Powell Tate Public Relations] in the next session said that grocery manufacturers are frequent subjects of unfair criticism and have nothing to apologize for.
Take that, you new foodists!
MARS must think it knows more than the FDA about how to label food packages. It is developing its own version of front-of-package labels. It volunteered to put calories on the front of its candies; its multi-pack candies ay 210 calories per serving on the front. That number, however, remains on the back of the small candy store packs. Mars’ new labeling plans use the complex scheme used in Europe. I’m guessing this is a bold attempt to head off what it thinks the FDA might do – traffic lights.
KRAFT announces that it is voluntarily reducing the sodium in its foods by 10% by 2012. Kraft’s Macaroni & Cheese (SpongeBob package) has 580 mg sodium per serving and there are two servings in one of those small boxes: 1160 in total. A 10% reduction will bring it down to 1050 mg within two years. The upper recommended limit for an adult is 2300 mg/day.
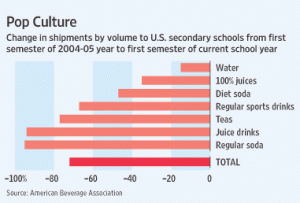
PEPSICO announced “a voluntary policy to stop sales of full-sugar soft drinks to primary and secondary schools worldwide by 2012.” In a press statement, the Yale Rudd Center quotes Kelly Brownell saying that “tobacco companies were notorious for counteracting declining sales in the U.S. with exploitation of markets elsewhere, particularly in developing countries:”
it will be important to monitor whether the mere presence of beverage companies in schools increases demand for sugared beverages through branding, even if full-sugar beverages themselves are unavailable…This appears to be a good faith effort from a progressive company and I hope other beverage companies follow their lead…this announcement definitely represents progress [Note: see clarification at end of post].
According to PepsiCo, this new policy brings its international actions in line with what it is already doing in the U.S. The policy itself is voluntary, uses words like “encourage,” assures schools that the company is not telling them what to do, and won’t be fully implemented until 2010. It keeps vending machines in schools and still allows for plenty of branded sugary drinks: Gatorade, juice drinks, and sweetened milk for example.
Could any of this have anything to do with Kelly Brownell’s forceful endorsement of soda taxes?
LOBBYING: The Center for Responsive Politics says food companies spent big money on lobbying last year, and notes an enormous increase in the amount spent by the American Beverage Association (soda taxes, anyone?). For example:
| American Beverage Assn |
$18,850,000 |
| Coca-Cola Co |
$9,390,000 |
| PepsiCo Inc |
$9,159,500 |
| Coca-Cola Enterprises |
$3,020,000 |
| National Restaurant Assn |
$2,917,000 |
| Mars Inc |
$1,655,000 |
|
How to view all this? I see the company promises as useful first steps. But how about the basic philosophical question we “new foodists” love to ask: “is a better-for-you junk food a good choice?”
OK. We have the Public Relations. Now let’s see what these companies really will do.
Addendum: I received a note clarifying Kelly Brownell’s role in the PepsiCo press release from Rebecca Gertsmark Oren,Communications Director,The Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity,Yale University:
The Rudd Center did not work with PepsiCo on their initiative to stop sales of full-sugar beverages in schools worldwide, nor did we jointly issue a press release. A statement released by Kelly Brownell in response to PepsiCo’s announcement was simply intended to commend what appears to be a step in the right direction. As Kelly’s statement also mentioned, there is still plenty of work to be done. It’s also worth noting that the Rudd Center does not take funding from industry.