| Contact: info@ruralamerica2020.org |
|
Iowa Farmers and Ag Leaders Demand that Senators Ernst and Grassley Release Secret List of Trump Ethanol Promises
Iowa Corn Farmer Doug Thompson: “Our Senators went to the White House, were made promises on ethanol that never came true, and then never said a word about it.”
Rural America 2020 Iowa Steering Committee writes letter to Ernst and Grassley; Group will be posting billboard advertisements and buying radio ads across Iowa calling for the release of the secret list of broken promises
(Des Moines, IA) –A group of Iowa farmers and ag leaders sent a letter to Iowa Senators Joni Ernst and Chuck Grassley today demanding that they make public a secret list of promises on federal ethanol policy that the Trump Administration made to them at the White House almost exactly one year ago.
This secret list of promises, the vast majority of which have not been fulfilled, was first reported by Reuters today and offers powerful evidence of the Trump administration’s failure to support ethanol, despite his rhetoric. This secret list also highlights how Senator Ernst and Grassley have failed to follow through on their own promises to fight for Iowa farmers with this administration, despite their rhetoric. Just last week, Senator Ernst touted herself as a “tireless advocate” for the ethanol industry yet by never releasing the list of White House ethanol promises she has avoided having to call out the President for the full extent of his failures.
“This is a betrayal on all sides,” said Iowa corn grower Doug Thompson, a member of the Rural America 2020 Iowa Steering Committee that sent the letter. “Our Senators went to the White House, were made promises on ethanol that never came true, and then never said a word about it. It’s a colossal failure of execution and accountability and the only people who got hurt are the Iowa farmers who have lost billions of gallons in ethanol demand.
“We are now less than two weeks away from Iowa voters beginning to vote.” Thompson also said. “Senators Ernst and Grassley owe it to all Iowa farmers and voters to immediately release the list of ethanol promises – that was made on White House letterhead – so that Iowans understand the full magnitude of Trump’s broken ethanol promises. It’s the only way we can hold them accountable going forward. Even if our Senators claim this was a preliminary list – which we have no indication it was – it should be made public so that Iowans can see the extent to which our home state Senators got rolled by Big Oil and the White House.”
Rural America 2020, which already has billboards up across Iowa decrying Trump’s broken ethanol promises, will be placing messages across the state demanding the release of the secret ethanol list. They will also be recording radio ads from Iowa farmers that call for release of the list.
A timeline of the events (and related reporting) around the White House meeting in which the list was shared is as follows:
August 9th, 2019 – Trump administration grants 31 waivers for oil refineries that help undercut demand for ethanol.
August 16th, 2019 – Senator Grassley says publicly that Trump’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)“screwed us” by providing 31 waivers to oil refiners.
August 23rd, 2019 – Senator Ernst says at a town hall meeting that the White House is putting together a document that will include all the help they will be providing on ethanol.
August 29th, 2019 – President Trump publicly promises corn farmers a “giant package” after angering them by providing the waivers.
September 12th, 2019 – White House convenes meeting with Senators Grassley and Ernst as well as Senators Ben Sasse (R-NE), Deb Fischer (R-NE), John Thune (R-SD), Mike Rounds (R-SD) and Governor Kim Reynolds. They are presented with the list of promises.
September 12th, 2019 – President Trump meets with the CEOs of Valero Energy (Joe Gorder) and Marathon Petroleum (Gary Heminger) to discuss Big Oil’s concerns on the same day as the meeting with the Senators and Governor Reynolds.
September 17th, 2019 – Grassley admits to having seen a “13-point plan” from the White House but declines to say what was in it or anything about it.
September 18th, 2019 – Both Grassley and Reynolds say they were encouraged by the White House meeting but that they want to see “something in writing” despite having both seen the secret list of promises in writing at the meeting on September 12th. Ernst also repeatedly tweets that she wants to see a plan in writing despite having seen the White House plan.
One year later – Brian Jennings, chief executive officer of the American Coalition for Ethanol says that “so many ethanol promises, promises to do right by this industry have collected dust” and says that recent attempts by the White House to manufacture ethanol policy victories “should never have been given credibility.”
“Over a year after receiving a list of promises from the White House – a ‘13-point plan’ as Senator Grassley referred to it – neither Ernst nor Grassley – has released the plan so that Iowans can judge for themselves,” added Doug Thompson. “Has the President broken even more promises than we know? Have our Senators spent the last year getting conned by the President or are they all just conning Iowa farmers? We need to see this list immediately to find out.”
The full text of the letter from the Iowa Steering Committee is below. The letter was sent to Senators Ernst and Grassley who attended the meeting at the White House where the ethanol promises were made. The Iowa Steering Committee also cc’d the other Senators at the meeting and Iowa Governor Kim Reynolds who also attended the meeting.
Dear Senators Ernst and Grassley:
On September 12th, 2019, the President promised you in writing that he would add 500 million gallons of ethanol and 500 million gallons of advanced biofuels to the 2020 supplemental blending rule. While this market access would have been a welcome buffer during turbulent times, it did not happen. He also promised to add 250 million gallons of biodiesel to the 2021 blending volumes, however, we are still waiting. Renewable Volume Obligations (RVOs) are typically released in the summer to be finalized in November, but nothing has been presented to producers and the public for 2021. It is now harvesting season and the end of 2020 is around the corner, yet farmers and biofuel producers have little insight on how to plan for the 2021 planting season.
It is time for the President to make good on his promises to you, if he ever will. While he has had a year since releasing a list of promises, the few kept have come on the heels of outcry from rural voters. We believe that you must release his list of promises made if we are to see him keep any of them in the next 40 days, or after. Given his track record, we are concerned a Trump second term will include few promises to farmers at all, let alone broken ones.
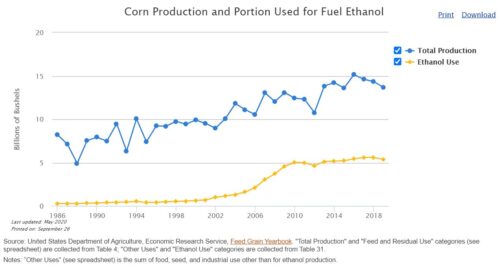
Over the past three years, farmers and biofuel producers have lost our greatest export markets and faced devastating blows in the name of Big Oil handouts. Small refinery waivers skyrocketed under Trump, slashing four billion gallons of biofuels from the market. Staff at 150 biofuel plants in America lost hours or their jobs entirely. One billion bushels of corn – on top of already stored crops thanks to trade disputes – did not get blended into ethanol, driving commodity prices down even further.
Thanks to Trump’s broken promises, rising input costs, and dwindling receipts farmers have been forced to live on government-aid bailouts of $12 billion, $16 billion, and most recently $14 billion. Farmers do not want cash bailouts. Our sales drive our communities and job creation. Our quality of life and long-term viability rely on sales, manufacturing and economic incentives – not government checks. We want export markets, a level playing field and the certainty that comes with planning. Unfortunately, this administration has failed the bare minimum – to carry out a plan.
As reported, the President’s written promises to you were guarantees to streamline compliance for E15, act to support expansion of E85, resolve trade disputes, and address E10 and E15 labeling. To date these promises have not been upheld, and year-round E15 is only sold at 2,000 of 152,000 U.S. retail stations. As the president continues to break his promises, we have little faith 2021 will meet the expressed guarantee of 15 billion gallons.
It is time you make his promises public. Doing so prior to an election is the only way to hold him accountable. After the election, as we have seen, the President is far more inclined to side with Big Oil. Now is the time to demand these promises be made public and that they be fulfilled. Biofuel producers and farmers in your home state are depending on it.
Sincerely,
Doug Thompson, Kanawha, Iowa
John Judge, Albia, Iowa
Chris Henning, Cooper, Iowa
Tom Grau, Newell, Iowa
Aaron Lehman, Polk City, Iowa
Marcella and William Frevert, Emmetsburg, Iowa
Tom Furlong, Letts, Iowa
CC:
U.S. Senator Ben Sasse
U.S. Senator Deb Fischer
U.S. Senator John Thune
U.S. Senator Mike Rounds
Governor Kim Reynolds |