Big Soda sues to hide its funding of anti-tax campaign
Sometimes the actions of food companies defy credulity.
Get this: The Community Coalition Against Beverage Taxes, a “grassroots” group funded by the American Beverage Association, has taken the city of Richmond, California to court to block it from requiring disclosure of funding sources in election campaigns.
In case you haven’t been following this situation, the Richmond city council got a soda tax initiative (“Measure N”) placed on the November ballot.
Richmond is a low-income, mixed-race city (80% non-white), with an 11% unemployment rate, and an average household income of $23,000 a year. It population is largely obese and drinks a lot of sodas.
You would hardly think a city like this would get on the radar of Big Soda, but you would be oh so wrong.
For details, we have to thank Robert Rogers who writes for the local Contra Costa Times.
Mr. Rogers has been following the money.
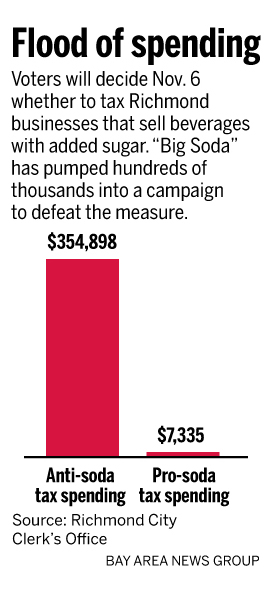
Because California requires lobbyists to register, he has been able to get hard numbers on the relative spending of anti-tax forces and those who favor the tax. The difference is impressive.
The city of Richmond must have suspected that something like this would happen because the city council passed an ordinance that requires special interest groups to disclose who funds them in campaign literature. They must list their top five funders.
You might think this idea entirely appropriate to a democratic society, but the American Beverage Association (translation: Coca-Cola and PepsiCo) does not.
According to Rogers’ account on September 4, Big Soda has sued the city in federal court to stop it from insisting that campaigns disclose who funds them.
On what grounds, pray tell?
The First Amendment, of course.
The suit, filed in federal court in San Francisco on Aug. 30, seeks an order barring the city from imposing its campaign ordinance on the Community Coalition Against Beverage Taxes, a declaration that the groups’ First Amendment rights were violated and money to cover court costs.
The coalition is funded mostly by the American Beverage Association and has spent more than $350,000 locally in an effort to defeat a November ballot measure that could impose a penny-per-ounce tax on sales of all sugar-sweetened beverages in the city.
…Coalition spokesman Chuck Finnie said Tuesday that the law itself is unconstitutional and should not be applied to the anti-soda tax groups.
“The law in question is being enforced to prevent opponents of an unfair, misleading and misguided tax from being able to communicate effectively with Richmond voters,” Finnie said. “The sponsors of the Measure N tax don’t want voters to hear how the tax is going to raise grocery bills, hurt local businesses on which livelihoods depend, and the fact that city politicians would be free to spend all of the money raised by Measure N in any way they see fit and that not one penny must be used to fund anti-obesity efforts.”
In other words, revealing funding sources prevents “effective communication.”
The court will hear this suit on Friday. Stay tuned.
In the meantime, here are the relevant documents, thanks to Robert Rogers.